Cross-Chain Bridges: The Gateways of Blockchain Interoperability
Unlocking liquidity across blockchains has transformed DeFi, but these connections come with trade-offs worth understanding deeply.
Introduction
Imagine holding ETH on Ethereum but spotting a high-yield opportunity on Solana—or wanting to use your Bitcoin as collateral in an Avalanche lending protocol. Without a way to move value seamlessly, the multi-chain world would remain fragmented, limiting innovation and liquidity.
Cross-chain bridges solve this isolation. They enable the transfer of tokens, data, and even messages between independent blockchains that don’t natively communicate. As DeFi TVL surpasses hundreds of billions in 2026, bridges have become essential infrastructure, powering everything from simple asset swaps to complex cross-chain applications.
Yet bridges are also among the riskiest components in crypto. Historical exploits have drained billions, highlighting that interoperability often requires careful trust assumptions. This evergreen guide breaks down the fundamentals: how bridges work step-by-step, the top protocols today, key mechanics like wrapped tokens and liquidity pools, common exploit vectors, and best practices for staying secure.
Whether you’re a DeFi participant bridging assets daily or a developer building on multi-chain ecosystems, understanding these timeless principles helps navigate the space confidently.
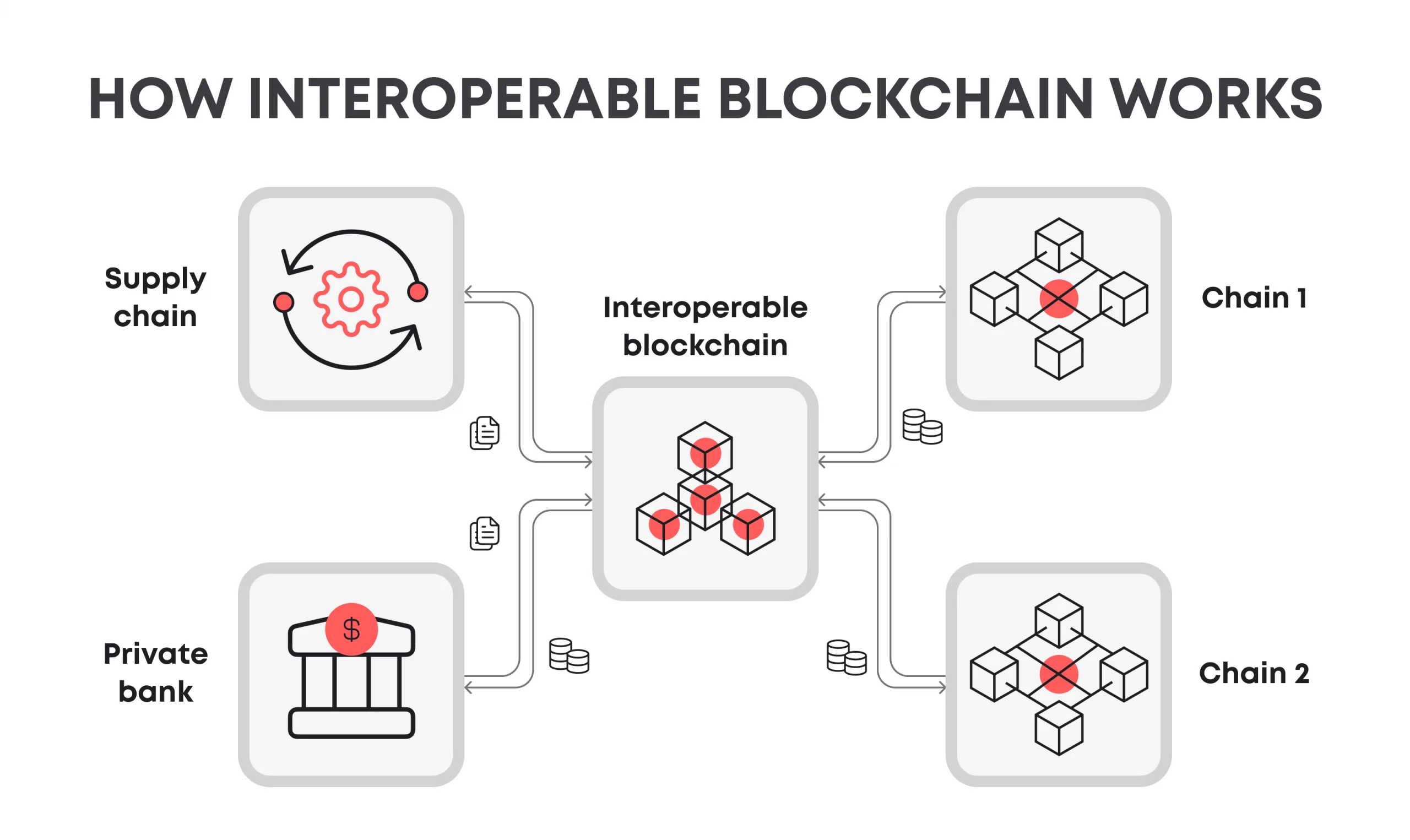
How Cross-Chain Bridges Work: Core Mechanics Explained
At their essence, bridges facilitate interoperability by verifying events on one chain and triggering actions on another. Most operate through one of three primary mechanisms:
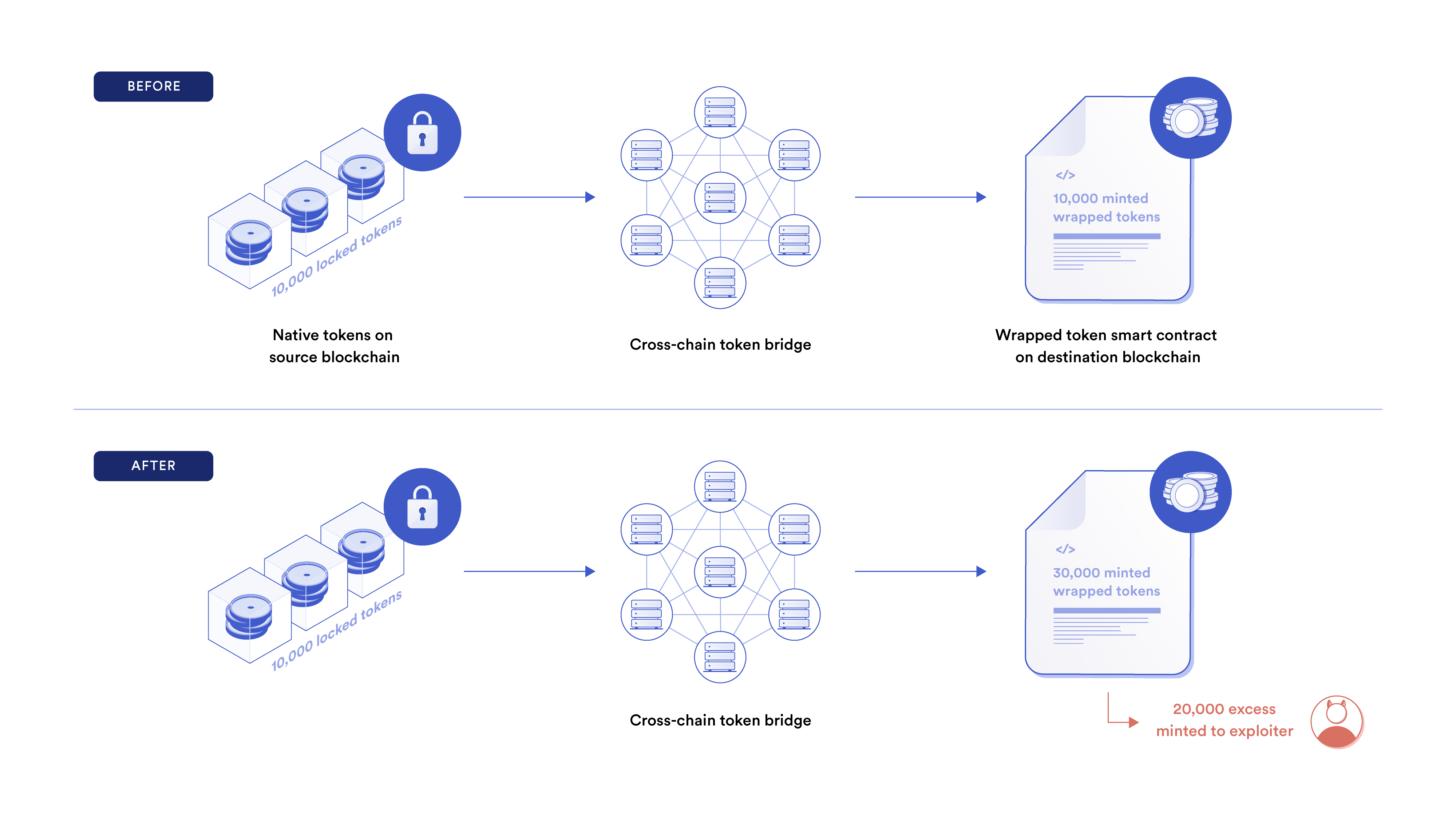
1. Lock-and-Mint (with Wrapped Tokens)
- User deposits native tokens into a bridge contract on the source chain—these are locked.
- The bridge verifies the lock and instructs a contract on the destination chain to mint equivalent wrapped tokens (e.g., wETH for ETH, wBTC for BTC).
- Reverse: Burn wrapped tokens to unlock originals.
This preserves pegged value while enabling use on foreign chains.
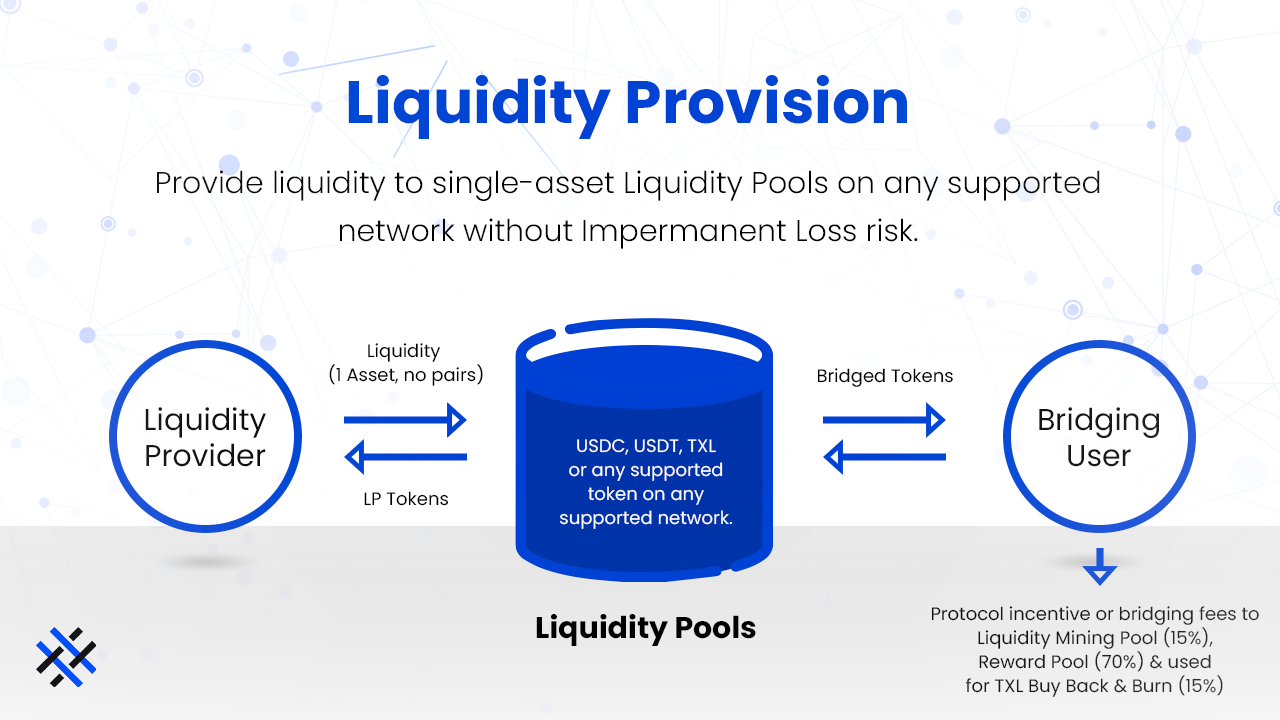
2. Liquidity Pool-Based (AMM-Style Swaps)
- Bridges maintain deep liquidity pools on both sides.
- User swaps into the pool on source; liquidity providers or automated routing release equivalent assets on destination.
- No wrapping needed for supported native assets; reduces slippage with incentives for providers.
3. Burn-and-Mint (Native Transfer)
- Tokens are permanently burned on source and freshly minted on destination.
- Common for native stablecoins (e.g., Circle’s CCTP for USDC).
- Irreversible but avoids wrapped token depeg risks.
Many modern bridges combine these with messaging layers (e.g., LayerZero, Axelar) for arbitrary data transfer, enabling cross-chain DeFi calls.
The Main Cross-Chain Bridges in 2026
The landscape evolves rapidly, but established protocols dominate by TVL, volume, and chain support. Here’s a snapshot of leading ones (based on DeFiLlama and industry reports as of early 2026):
| Bridge | Type | Key Chains Supported | Strengths | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stargate | Liquidity Network (LayerZero) | 20+ EVM + some non-EVM | Unified liquidity, low slippage | Native assets, fast finality |
| Synapse | Liquidity + Messaging | 30+ including Solana, Ethereum L2s | Versatile, NFT support | Competitive fees, high TVL |
| Wormhole (Portal) | Validator-Based Messaging | Broad (Solana, EVM, others) | Wide adoption, data messaging | Recovered from past exploits |
| Across | Intents-Based Optimistic | Ethereum L2 focus + majors | Ultra-fast, low fees | No pooled liquidity risk |
| Symbiosis | Aggregator + Liquidity | 30+ EVM/non-EVM | One-click swaps, broad pairs | User-friendly UI |
| THORChain | Liquidity Pool (Native Swaps) | Bitcoin, ETH, others (non-custodial) | True native-to-native | Decentralized, no wrapping |
| deBridge | Intents + Zero-TVL | Multiple | High speed, low spreads | Developer-focused |
These handle billions in monthly volume, with intents-based designs (Across, deBridge) gaining traction for speed and capital efficiency.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Bridges power:
- Yield Migration: Move stablecoins to highest APY chains.
- Cross-Chain DeFi: Borrow on Aave (Ethereum) using collateral from Polygon.
- NFT Mobility: Transfer assets between gaming ecosystems.
Successful implementations include Stargate’s integration with major DEXs and THORChain’s native Bitcoin swaps—proving non-custodial interoperability at scale.
Risks and Common Exploit Vectors
Bridges have suffered massive losses—over $2.8 billion historically, often dominating DeFi hacks.

Key vectors:
- Validator/Guardian Compromise: Private key theft (Ronin 2022: $625M; Wormhole 2022: $320M).
- Smart Contract Bugs: Infinite minting or faulty verification (Nomad 2022: $190M).
- Oracle/Manipulation Issues: False event proofs.
- Centralization Risks: Multisig thresholds too low.
- Liquidity Attacks: Draining pools via flash loans.
Even audited bridges aren’t immune—upgrades or off-chain components introduce risks.
Secure Design Principles and Best Practices
To mitigate risks:
For Developers/Builders
- Multiple independent audits + ongoing bug bounties.
- Decentralized validation (e.g., diverse node operators).
- Rate limits, timelocks, and emergency pauses.
- Minimize trust: Use optimistic/intents models over pooled liquidity.
- Formal verification for critical code.
For Users/DeFi Participants
- Start small: Test transfers with minimal amounts.
- Choose audited, high-TVL bridges with transparent history.
- Verify contract addresses; avoid phishing sites.
- Monitor for upgrades or incidents via official channels.
- Diversify: Don’t concentrate assets in one bridge.
- Revoke approvals post-transfer.
Emerging standards like Chainlink CCIP emphasize risk management networks for added oversight.
Future Outlook
Interoperability is maturing: Zero-knowledge proofs promise trustless bridges, intents simplify UX, and native messaging expands composability. Yet the core trade-off remains—faster/cheaper often means more assumptions.
As chains proliferate, robust bridges will define winners in the multi-chain era.
Conclusion
Cross-chain bridges are the unsung connectors making blockchain’s fragmented world feel unified. They unlock immense value but demand vigilance given their attack surface.
Approach them informed: Understand mechanics, weigh risks against rewards, and follow secure practices. In DeFi’s evolving landscape, knowledgeable users thrive.
Explore more evergreen guides on blockchain fundamentals, DeFi mechanics, and risk management. Subscribe to Cryptopress.site for timeless insights into cryptocurrency and blockchain education. What bridge do you use most—and why? Share in the comments.
© Cryptopress. For informational purposes only, not offered as advice of any kind.
Latest Content
- Crypto Weekly Snapshot – Strong Start to 2026
- US Forces Capture Maduro in Swift Raid. Activity on Polymarket Skyrockets Over Possible Outcomes
- Cross-Chain Bridges: The Gateways of Blockchain Interoperability
- Shiny Coins #3 – Bloodbath Survivors Rise from the Ashes
- Aave Labs Proposes Non-Protocol Revenue Sharing to Ease DAO Governance Tensions
Related
- What are ‘wrapped tokens’? Wrapped tokens are a type of tokenized cryptocurrency....
- PancakeSwap Introduces a Major Leap in DeFi Interoperability with its PancakeSwap Bridge: Enabling Fast, Secure, Cross-Chain Transfers Across 8 Chains and over 3700+ Tokens, Powered by BNB Chain PancakeSwap has just launched the PancakeSwap Bridge....
- Top 10 Best Staking Coins for Passive Income in 2026 Discover the best staking coins for 2026 passive income. Compare crypto staking rewards, APY rates & top coins for earning cryptocurrency yields....
- Non-Fungible Tokens: The Guide Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are a new type of token which is represented by unique cryptographic units, meaning that each token has a unique value. ...